ActSonic: Recognizing Everyday Activities from Inaudible Acoustic Waves Around the Body
Published in The Proceedings of the Association for Computing Machinery on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT)/UbiComp, 2024
Recommended citation: Saif Mahmud, Vineet Parikh, Qikang Liang, Ke Li, Ruidong Zhang, Ashwin Ajit, Vipin Gunda, Devansh Agarwal, François Guimbretière, and Cheng Zhang. 2024. ActSonic: Recognizing Everyday Activities from Inaudible Acoustic Waves Around the Body. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 8, 4, Article 183 (November 2024), 32 pages. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3699752
November 2024
Keyword: Acoustic Sensing, Activity Recognition, Self-supervised Leaning
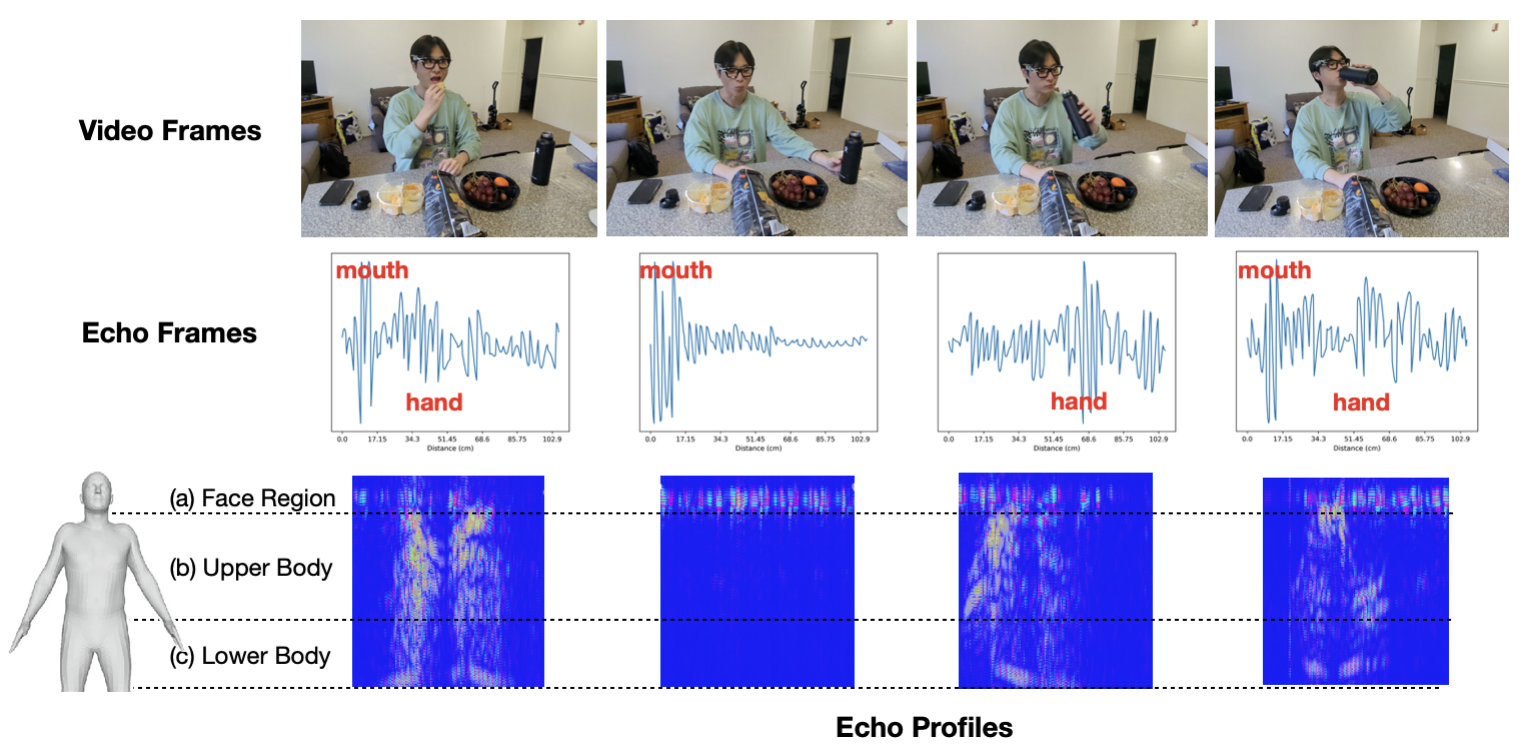
We present ActSonic, an intelligent, low-power active acoustic sensing system integrated into eyeglasses that can recognize 27 different everyday activities (e.g., eating, drinking, toothbrushing) from inaudible acoustic waves around the body with a time resolution of one second. It only needs a pair of miniature speakers and microphones mounted on each hinge of eyeglasses to emit ultrasonic waves to create an acoustic aura around the body. Based on the position and motion of various body parts, the acoustic signals are reflected with unique patterns captured by the microphone and analyzed by a customized self-supervised deep learning framework to infer the performed activities. ActSonic was deployed in a user study with 19 participants across 19 households to evaluate its efficacy. Without requiring any training data from a new user (leave-one-participant-out evaluation), ActSonic was able to detect 27 activities, achieving an average F1-score of 86.6% in fully unconstrained scenarios and 93.4% in prompted settings at participants’ homes.
