GazeTrak: Exploring Acoustic-based Eye Tracking on a Glass Frame
Published in The Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom), 2024
Recommended citation: Ke Li, Ruidong Zhang, Boao Chen, Siyuan Chen, Sicheng Yin, Saif Mahmud, Qikang Liang, Francois Guimbretiere, and Cheng Zhang. 2024. GazeTrak: Exploring Acoustic-based Eye Tracking on a Glass Frame. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 497–512. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3636534.3649376
Selected Media Coverage: New Scientist, Forbes, Cornell Chronicle
November 18-22, 2024, Washington, D.C., USA
Keyword: Eye Tracking, Acoustic Sensing, Smart Glasses, Low-power
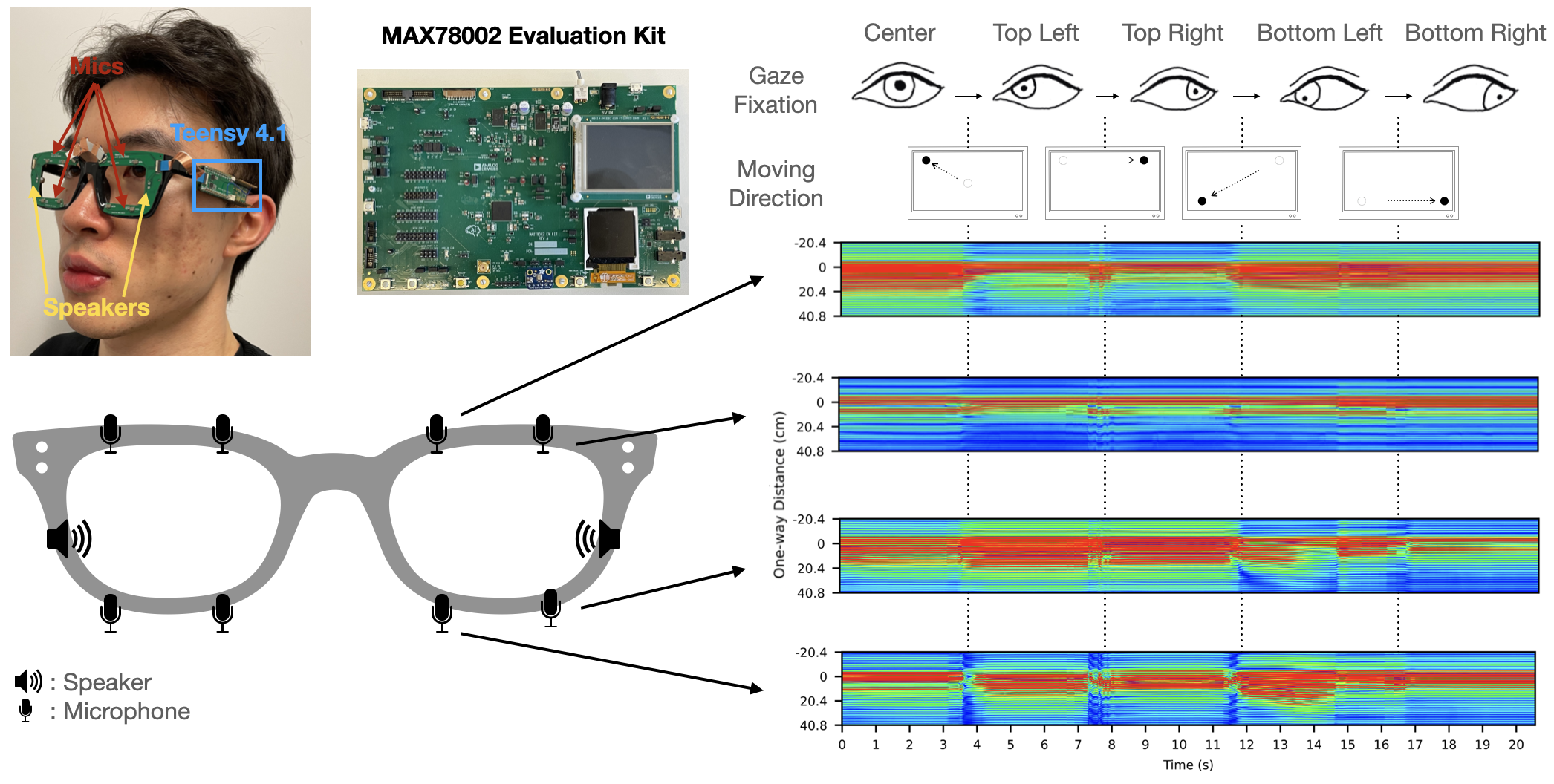
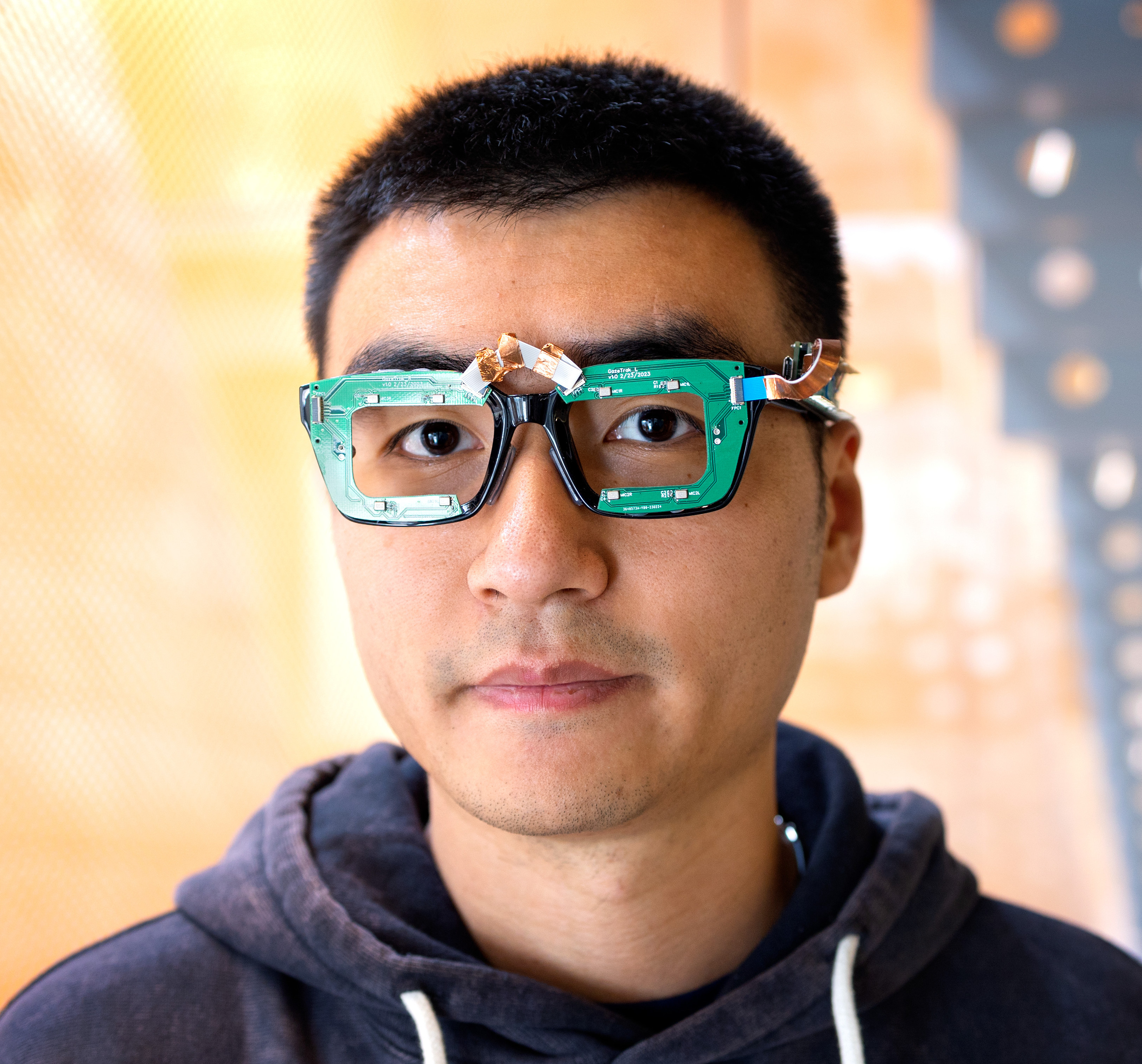
In this paper, we present GazeTrak, the first acoustic-based eye tracking system on glasses. Our system only needs one speaker and four microphones attached to each side of the glasses. These acoustic sensors capture the formations of the eyeballs and the surrounding areas by emitting encoded inaudible sound towards eyeballs and receiving the reflected signals. These reflected signals are further processed to calculate the echo profiles, which are fed to a customized deep learning pipeline to continuously infer the gaze position. In a user study with 20 participants, GazeTrak achieves an accuracy of 3.6° within the same remounting session and 4.9° across different sessions with a refreshing rate of 83.3 Hz and a power signature of 287.9 mW. Furthermore, we report the performance of our gaze tracking system fully implemented on an MCU with a low-power CNN accelerator (MAX78002). In this configuration, the system runs at up to 83.3 Hz and has a total power signature of 95.4 mW with a 30 Hz FPS.
