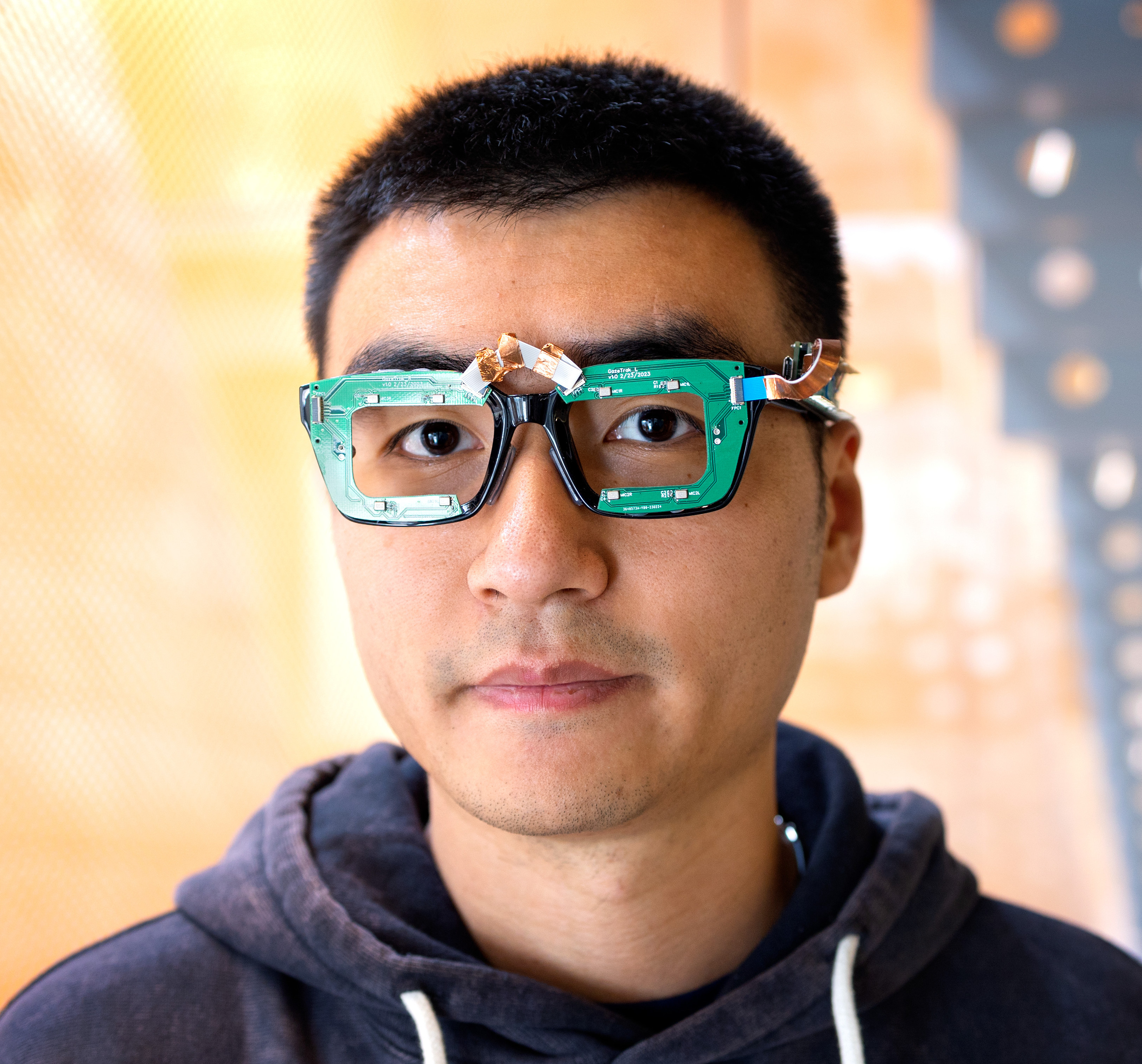
PoseSonic: 3D Upper Body Pose Estimation Through Egocentric Acoustic Sensing on Smartglasses
Published in The Proceedings of the Association for Computing Machinery on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT)/UbiComp, 2023
Recommended citation: Saif Mahmud, Ke Li, Guilin Hu, Hao Chen, Richard Jin, Ruidong Zhang, François Guimbretière, and Cheng Zhang. 2023. PoseSonic: 3D Upper Body Pose Estimation Through Egocentric Acoustic Sensing on Smartglasses. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 3, Article 111 (September 2023), 28 pages. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3610895
Selected Media Coverage: Cornell Chronicle
October 8-12, 2023, Cancún, Mexico
Keyword: Human Pose Estimation, Acoustic Sensing, Smart/AR Glasses, Deep Learning, Cross-Modal
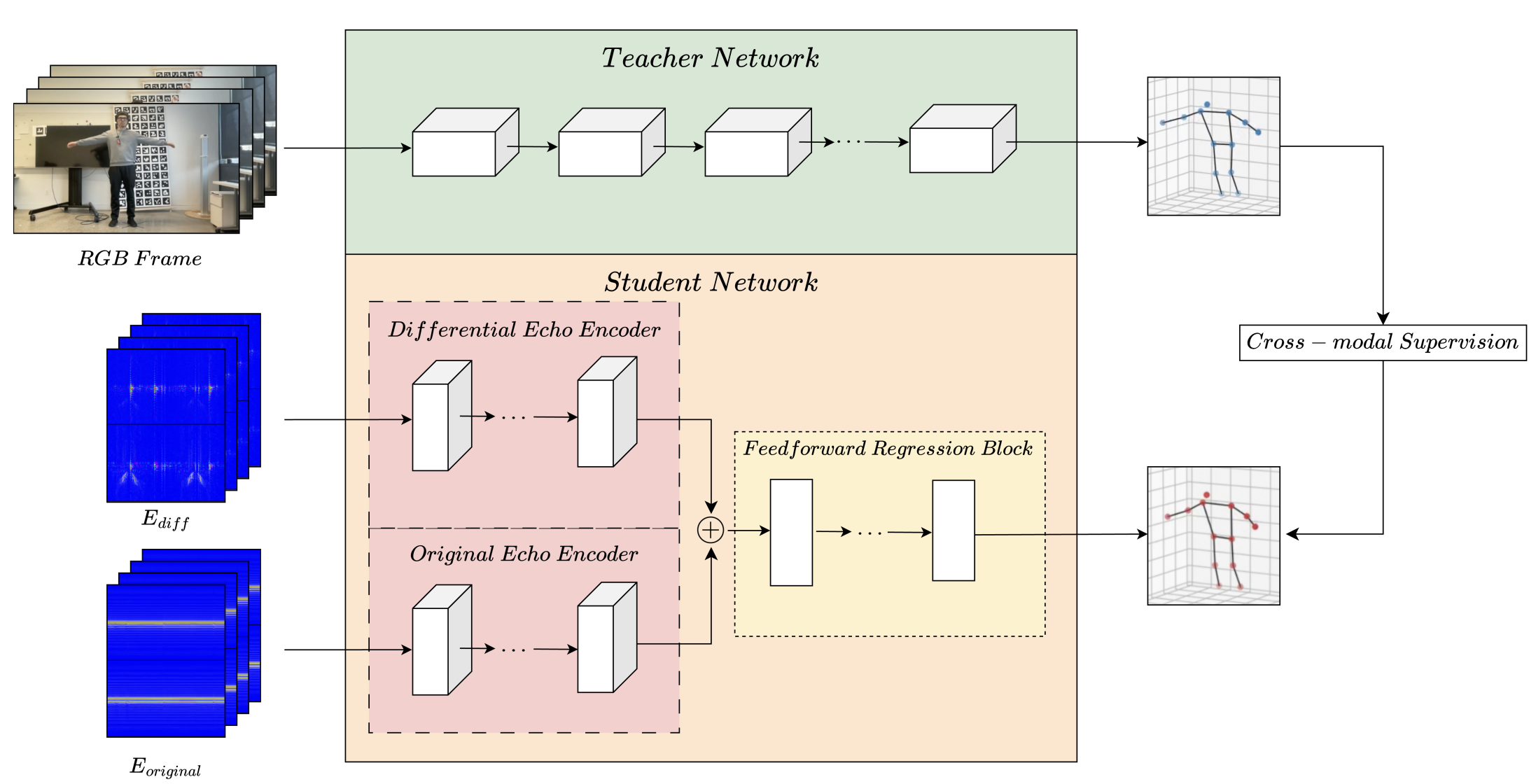
In this paper, we introduce PoseSonic, an intelligent acoustic sensing solution for smartglasses that estimates upper body poses. Our system only requires two pairs of microphones and speakers on the hinges of the eyeglasses to emit FMCW-encoded inaudible acoustic signals and receive reflected signals for body pose estimation. Using a customized deep learning model, PoseSonic estimates the 3D positions of 9 body joints including the shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, and nose. We adopt a cross-modal supervision strategy to train our model using synchronized RGB video frames as ground truth. We conducted in-lab and semi-in-the-wild user studies with 22 participants to evaluate PoseSonic, and our user-independent model achieved a mean per joint position error of 6.17 cm in the lab setting and 14.12 cm in semi-in-the-wild setting when predicting the 9 body joint positions in 3D. Our further studies show that the performance was not significantly impacted by different surroundings or when the devices were remounted or by real-world environmental noise. Finally, we discuss the opportunities, challenges, and limitations of deploying PoseSonic in real-world applications.
